Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM84ZXF)
| Drug Name |
Lorazepam
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Almazine; Alzapam; Anxiedin; Anxira; Anzepam; Aplacasse; Aplacassee; ApoLorazepam; Aripax; Ativan; Azurogen; Bonatranquan; Bonton; Delormetazepam; Demethyllormetazepam; Donix; Duralozam; Durazolam; Efasedan; Emotion; Emotival; Equitam; Idalprem; Kalmalin; Larpose; Laubeel; Lomesta; Lopam; Lorabenz; Lorafen; Loram; Lorans; Lorapam; Lorat; Lorax; Loraz; Lorazene; Lorazep; Lorazepamum; Lorazin; Lorazon; Lorenin; Loridem; Lorivan; Lorsedal; Lorsilan; Lorzem; Lozepam; Merlit; Nervistopl; Norlormetazepam; Novhepar; Novolorazem; NuLoraz; Orfidal; Punktyl; Quait; Renaquil; Rocosgen; Securit; Sedatival; Sedazin; Sedicepan; Sedizepan; Sidenar; Silence; Sinestron; Somagerol; Stapam; Tavor; Temesta; Tolid; Tranqipam; Trapax; Upan; Vigiten; Wypax; AHP Brand of Lorazepam; Apo Lorazepam; Apotex Brand of Lorazepam; Baxter Brand of Lorazepam; Ct Arzneimittel Brand of Lorazepam; Desitin Brand of Lorazepam; Dolorgiet Brand of Lorazepam; Llorens Brand of Lorazepam; Lorazep von ct; Lorazepam AHP Brand; Lorazepam Apotex Brand; Lorazepam Baxter Brand; Lorazepam Desitin Brand; Lorazepam Dolorgiet Brand; Lorazepam Fabra; Lorazepam Genericon; Lorazepam Intensol; Lorazepam Lannacher; Lorazepam Llorens Brand; Lorazepam Medical; Lorazepam Medical Brand; Lorazepam Medix Brand; Lorazepam Novartis Brand; Lorazepam Novopharm Brand; Lorazepam Riemser Brand; Lorazepam Wyeth Brand; Lorazepam neuraxpharm; Lorazepam neuraxpharm Brand; Lorazepam preservative free; Lorazepam ratiopharm; Lorazepam ratiopharm Brand; Lorazepan Chobet; Lorazepan Richet; Max Pax; Medical Brand of Lorazepam; Medix Brand of Lorazepam; Merck dura Brand of Lorazepam; Nervistop L; Neuraxpharm Brand of Lorazepam; Novartis Brand of Lorazepam; Novo Lorazem; Novopharm Brand of Lorazepam; Nu Loraz; Nu Pharm Brand of Lorazepam; Orfidal Wyeth; Pro dorm; Ratiopharm Brand of Lorazepam; Riemser Brand of Lorazepam; Serra Pamies Brand of Lorazepam; Wyeth Brand of Lorazepam; L1764_SIGMA; WY4036; Wy 4036; Apo-Lorazepam; Ativan (TN); Ct-Arzneimittel Brand of Lorazepam; Lorazepam (Ativan); Lorazepam Nu-Pharm Brand; Lorazepam ct-Arzneimittel Brand; Lorazepam-Efeka; Lorazepam-neuraxpharm; Lorazepam-ratiopharm; Lorazepamum [INN-Latin]; Medical, Lorazepam; Novo-Lorazem; Nu-Loraz; Nu-Pharm Brand of Lorazepam; O-Chlorooxazepam; O-Chloroxazepam; Temesta (TN); Wy-4036; Wyeth, Orfidal; Lorazepam (JP15/USP/INN); Lorazepam [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN]; (+-)-7-Chloro-5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one; (+/-)-Lorazepam; 7-Chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one; 7-Chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one; 7-Chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxy-1H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2(3H)-one; 7-Chloro-5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one; 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antianxiety Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
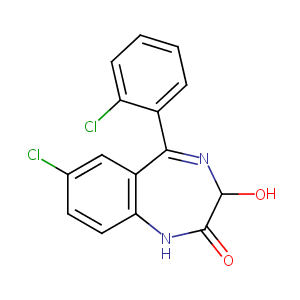 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 321.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Lorazepam (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Lorazepam FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5884). | ||||
| 3 | Matzke GR, Zhanel GG, Guay DR: Clinical pharmacokinetics of vancomycin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1986 Jul-Aug;11(4):257-82. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198611040-00001. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Li C, Liu T, Cui X, Uss AS, Cheng KC: Development of in vitro pharmacokinetic screens using Caco-2, human hepatocyte, and Caco-2/human hepatocyte hybrid systems for the prediction of oral bioavailability in humans. J Biomol Screen. 2007 Dec;12(8):1084-91. doi: 10.1177/1087057107308892. Epub 2007 Nov 7. | ||||
| 6 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 7 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 8 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 9 | Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interaction of lorazepam and valproic acid in relation to UGT2B7 genetic polymorphism in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008 Apr;83(4):595-600. | ||||
| 10 | Effect of the UGT2B15 genotype on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and drug interactions of intravenous lorazepam in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Jun;77(6):486-94. | ||||
| 11 | Chun AH, Carrigan PJ, Hoffman DJ, Kershner RP, Stuart JD "Effect of antacids on absorption of clorazepate." Clin Pharmacol Ther 22 (1977): 329-35. [PMID: 19188] | ||||
| 12 | US Food and Drug Administration "FDA warns about serious risks and death when combining opioid pain or cough medicines with benzodiazepines requires its strongest warning.". | ||||
| 13 | Product Information. Alinia (nitazoxanide). Romark Laboratories L.C., Tampa, FL. | ||||
| 14 | US Food and Drug Administration "FDA warns about serious risks and death when combining opioid pain or cough medicines with benzodiazepines requires its strongest warning.". | ||||
| 15 | Warrington SJ, Ankier SI, Turner P "Evaluation of possible interactions between ethanol and trazodone or amitriptyline." Neuropsychobiology 15 (1986): 31-7. [PMID: 3725002] | ||||
| 16 | Gill SS, Wright EM, Reilly CS "Pharmacokinetic interaction of propofol and fentanyl: single bolus injection study." Br J Anaesth 65 (1990): 760-5. [PMID: 2265045] | ||||
| 17 | Divoll M, Greenblatt DJ, Lacasse Y, Shader RI "Benzodiazepine overdosage: plasma concentrations and clinical outcome." Psychopharmacology (Berl) 73 (1981): 381-3. [PMID: 6789361] | ||||
| 18 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 19 | Backman JT, Olkkola KT, Ojala M, Laaksovirta H, Neuvonen PJ "Concentrations and effects of oral midazolam are greatly reduced in patients treated with carbamazepine or phenytoin." Epilepsia 37 (1996): 253-7. [PMID: 8598183] | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Alphagan (brimonidine ophthalmic). Allergan Inc, Irvine, CA. | ||||
| 21 | Castillo-Ferrando JR, Garcia M, Carmona J "Digoxin levels and diazepam." Lancet 2 (1980): 368. [PMID: 6105500] | ||||
| 22 | Andrews C, Pinner G "Postural hypotension induced by paroxetine." BMJ 316 (1998): 595. [PMID: 9518913] | ||||
| 23 | Hawksworth G, Betts T, Crowe A, et al "Diazepam/beta-adrenoceptor antagonist interactions." Br J Clin Pharmacol 17 Suppl 1 (1984): s69-76. [PMID: 6146341] | ||||
| 24 | Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Ameer B, Shader RI "Probenecid impairment of acetaminophen and lorazepam clearance: direct inhibition of ether glucuronide formation." J Pharmacol Exp Ther 234 (1985): 345-9. [PMID: 4020675] | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Zulresso (brexanolone). Sage Therapeutics, Inc., Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Addyi (flibanserin). Sprout Pharmaceuticals, Raleigh, NC. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Thalomid (thalidomide). Celgene Corporation, Warren, NJ. | ||||
| 29 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Gattex (teduglutide). NPS Pharmaceuticals, Bedminster, NJ. | ||||
| 31 | Hansen BS, Dam M, Brandt J, et al "Influence of dextropropoxyphene on steady state serum levels and protein binding of three anti-epileptic drugs in man." Acta Neurol Scand 61 (1980): 357-67. [PMID: 6998251] | ||||
| 32 | Sekar M, Mimpriss TJ "Buprenorphine, benzodiazepines and prolonged respiratory depression." Anaesthesia 42 (1987): 567-8. [PMID: 3592200] | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Zanaflex (tizanidine). Acorda Therapeutics, Hawthorne, NY. | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Zyrtec (cetirizine). Pfizer US Pharmaceuticals, New York, NY. | ||||
| 35 | Kerin NZ, Aragon E, Faitel K, Frumin H, Rubenfire M "Long-term efficacy and toxicity of high- and low-dose amiodarone regimens." J Clin Pharmacol 29 (1989): 418-23. [PMID: 2661600] | ||||
